
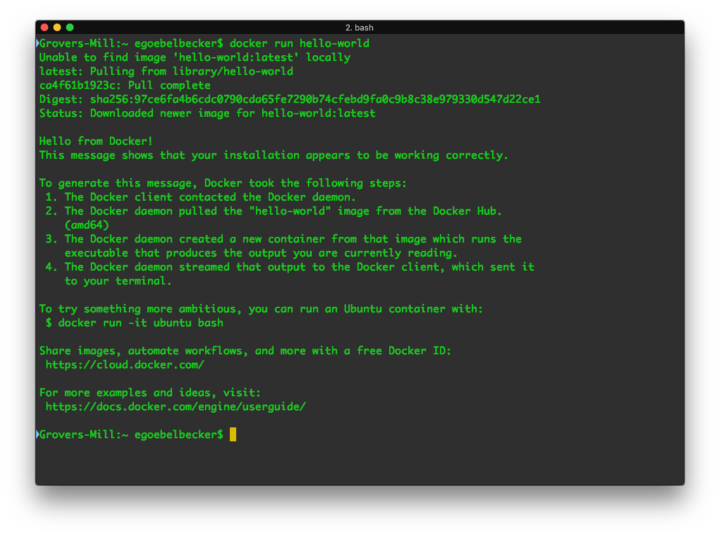
Docker run -it imagename sh Or following for images with an entrypoint. For example, you can pull an image that runs a Django server container to test how your application will interact with your production environment. Depending on your development needs, you can use Docker for the following: Pull pre-built images from a Docker registry. Docker images are executable packages for running containers. You can create and run a container with the following command:
DOCKER RUN IMAGE IN CONTAINER HOW TO
Here we discuss How to list images in Docker and Examples along with the outputs.So, if you are new to Docker, you might wonder how to run a docker container. We mostly use the “–format’ option to automate as it provides us output how we need it. The parent command of this command is the ‘docker image’. The shortest and easiest command to list the Docker images is the ‘docker images. It is possible in two ways, the first one is by using the ‘–quiet’ or the “-q” option, and the second one is by using the “–format” option by using the Go template as explained earlier, however, the ‘–quiet’ option is easy to use and fast. It can be done by using the “–no-trunc” option as shown below:Įxplanation: – In the above snapshot, we can see that there is only one DIGEST shown if the ‘–no-trunc” is not used however, when we use the “–no-trunc” option, we get one more digest that is truncated in the previous example. We want to show all output of the Docker images without truncating them.
We can use the ‘–format’ option to manipulate the output using the Go template for example, if we only want to list the name of the repository with the tag, we can use the ‘–format’ option as below:ĭocker images -format “".We can also use the ‘before’ or ‘since’ condition to list the images pulled before the specified image or after the specified image as below:įormat the output of the ‘docker image list’ command.We can create a container and force remove the image that is used by the container and run the above command again to get the dangling image. Note – if the above command does not show any output, there is no dangling image.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
